OECD GDP growth slows to 0.7% in the fourth quarter of 2020, with year-on-year falls for almost all countries

Following the unprecedented falls in the first half of 2020, due to COVID-19 containment measures, and the large rebound in the third quarter, growth of real gross domestic product (GDP) in the OECD area slowed to 0.7% in the fourth quarter of 2020, according to provisional estimates.
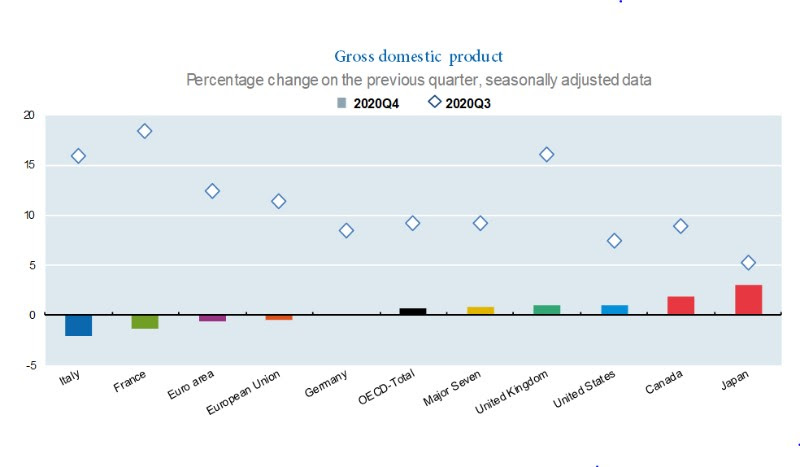
For the Major Seven economies as a whole, GDP growth slowed to 0.8% in the fourth quarter of 2020, with quite divergent patterns across countries. GDP growth remained positive in Japan (3.0%), Canada (1.9%), the United States and the United Kingdom (1.0% in both countries), and Germany (0.1%). In the other Major Seven economies, Italy and France, GDP fell (minus 2.0% and minus 1.3%, respectively), after strong rebounds in the previous quarter (16.0% and 18.5%, respectively).
In the euro area and the European Union, GDP contracted in the fourth quarter of 2020 by (minus) 0.6% and (minus) 0.4% respectively, following rebounds of 12.4% and 11.5% in the previous quarter.
For 2020 as a whole, GDP declined by (minus) 4.9% in the OECD area, which is the largest fall ever recorded (since 1962). Almost all countries were confronted with falls in GDP in 2020. Among the Major Seven economies, GDP declines ranged from (minus) 3.5% in the United States to (minus) 9.9% in the United Kingdom. Marked falls in GDP were also recorded in France (minus 8.2%) and Italy (minus 8.9%).
See the full release.
Visit the interactive OECD Data Portal to explore this data further.
Working with over 100 countries, the OECD is a global policy forum that promotes policies to improve the economic and social well-being of people around the world.












